Private Credit Back Leverage
Private Credit Back Leverage on the other hand is Non-Banking Credit and it has expanded over the past decade particularly after the global financial crises of 2008. This growth has been attributed to several reasons including increased bank scrutiny high return on cost seeking investors and organizations seeking for non-bank financing. There is one of the mechanisms that has appeared in the efforts to maximize the returns for this type of work and this is Private Credit Back Leverage.
In the following article we’ll look in to the subject of Private Credit Back Leverage in it and its advantages and disadvantages. We will also look at the effects of the minimum leverage ratios in investors and lending institutions.
What is Private Credit?
It may also include credits extended by non-port folioing companies which are not publicly traded like private equity houses hedge funds direct lenders among others. These loans are typically targeted at the middle market corporations which are too large for conventional small business loans yet too small to conduct bond or equity offering on public exchanges.
1. Direct lending
The facilities own-bought and given to companies by a private credit fund.
2. Mezzanine financing
A cross between a debt and an equity security and provides the issuer company with funding while not offering the buyer an ownership stake in the business.
3. Distressed debt
Bailing out or providing loans to distressed firms or firms going through or in the process of going through restructuring.
4. Special situations financing
Secured loans- most of which are tailored to meet the peculiar specific and temporary needs of a business.
Private credit is appealing to investors because they are expected to deliver higher yields as compared to standard fixed income securities especially during an environment characterized by low interest rates. However as we have seen higher return potential accompanying private credit to companies also increases risk as compared to public markets as private credit financing is usually given to companies with lower credit rating than companies servicing public bonds markets.
What is Back Leverage?
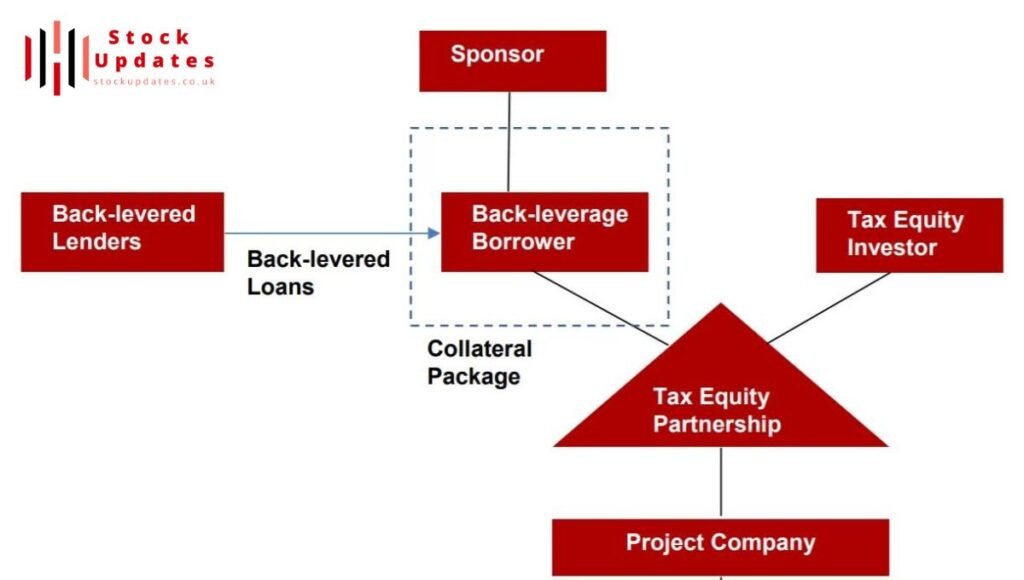
Back leverage on the actual means refers to the act of obtaining extra funds with an aim of boosting the possibilities of making profits from an investment portfolio. Looking at private credit especially back leverage can help the fund managers increase the returns they provide to investors.
For instance a private credit fund maybe provides a $100 million credit facility to a company. So that they can enhance their return on equity the fund may use back leverage to borrow $50 million from a third party investor which means the additional capital that is available for funding or investment. Thus they can leverage on the returns to the original investment.
Although this approach may give the fund higher returns it also means that the fund incurs more risks. In periods where the investments generate lower returns or when the fund experiences a shortage of cash back-leveraged debt actually augments the extent of the loss.
Essentials of Backing for Private Credit
Back leverage refers to getting a loan at a more attractive interest rate than the rate that is offered by the private credit fund. For instance while a private credit fund earns 10% on interest on the loan it obtained leverage at 5% reinforcement of the difference between the cost of borrowing and the return on the loan can be beneficial to the overall equity holders of the fund.
1. Initial loan amount
Holding of assets in the form of one hundred million dollars bonds bearing 10% interest.
2. Back leverage borrowed
The fund earns 10% on the whole sum of $100 million that is $10 million of interest income.
However the fund has only $50 million as the equity of the organization. Through back leverage at a fixed interest rate of 5% the fund borrows $ 50 million and thus it incurs $2. 5 million in interest on that loan It could be through an alternative channel such as over the internet through the mail or perhaps through deposits.
The other component of the net operating income is the net interest income of $10 million – $2. 5 million = $7. 5 million which is 15 percent of the fund’s equity the total equities of the fund is $ 50million.
Back Leverage Impact on Returns
| Item | Without Back Leverage | With Back Leverage |
| Total Loan Extended | $100 million | $100 million |
| Total Interest Earned (10%) | $10 million | $10 million |
| Equity Investment | $100 million | $50 million |
| Back Leverage Borrowed | $0 | $50 million |
| Interest on Back Leverage (5%) | $0 | $2.5 million |
| Net Interest Income | $10 million | $7.5 million |
| Return on Equity | 10% | 15% |
Risks Associated with Back Leverage
1. Increased Risk of Default
Back leverage entails the following risk this primarily involves the possibility of default in case the investments fail to pay out -as planned. In the case where loans offered by the private credit fund perform poorly the additional funds obtained through back leverage for efficiency become difficult to meet.
2. Liquidity Risk
Moreover back leverage also creates liquidity threats by having interest burden is usually required on the borrowed money. If there are problems with the borrowers’ payments the fund may face problems with its liquidity they might have to sell assets at a lower price.
3. Higher Volatility
Leverage works in the sense that it increases returns but it also acts in the same manner in increasing the losses. Private credit funds which employ back leverage come under higher market risks during volatile market conditions hence depicting high fluctuation of returns. This fluctuation can sometime make the private credit funds less certain than the non-leveraged type of private funds.
4. Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is a common risk to funds that employs back leverage in their working. When interest rates increase back leverage borrowing costs increase along with the fund’s yields on its loans while the difference between the two shrinks. In extreme forces this could actually eliminate all potential of making any profit in the leveraged investments.
5. Regulatory Risk
As the private credit market progresses there is raising attention from the regulators. Specific modifications in rules related to leverage or lending may affect facilities of private credit funds for employing back leverage. For example if the regulators set new harsher standards that force funds to have more equity capital or limit the amount that they can leverage back such a change will limit the use of this backs leverage strategy.
Impact of Minimum Leverage Requirements
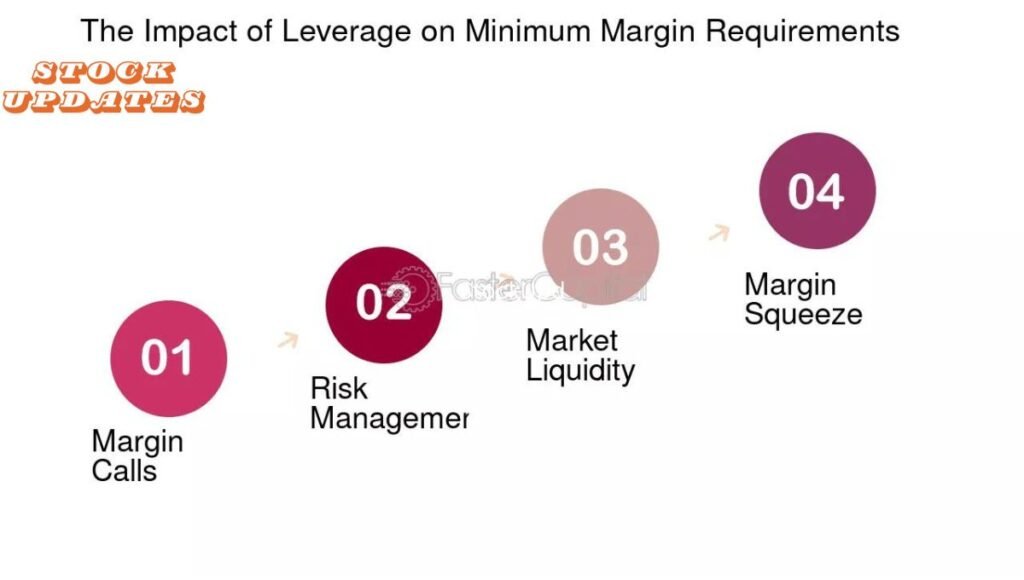
A number of lenders also require private credit funds to have minimum leverage amounts typically proportionate with the perceived risk in the underlying loans. These requirements hold the fund at a minimum threshold of equity as compared to borrowed capital which decreases with back leverage some risks.
Leverage is a potentially attractive means to enhance the returns of private credit funds (all else being equal) but minimum leverage requirements can prevent such instruments from fully maximizing their return potential through leveraging.
Benefits of Back Leverage
Although the risks of back leverage are quite large there is a list of advantages that make it an appealing approach to private credit funds as well:
1. Superior Returns
As discussed before back leverage can appreciably increase EQ returns at private credit funds. That has made it a popular choice for yield-hungry investors in today`s low-interest rate world.
2. Addition of leverage
Private credit funds can introduce back-to-back with their clients which allows them to increase the amount they have lendable. Diversification can limit the risk of default as returns in a diversified portfolio are dependent on several loans compared to just one.
Conclusion
It is yet another example of how private credit has become an important part of the financial landscape providing market-sourced funding to companies that do not want bank debt and return-seeking opportunities for investors who need a little more yield on their hard-earned savings. However fire spinner interest income alone does not manifest the kind of returns that investors typically expect from private credit funds. Back leverage is a potent way to juice these yields but involves considerable risk as well.
Imposing minimum leverage limits can also reduce these risks by maintaining a proper level of spread between the borrowed and equity capital available to each Fund. Nonetheless fund managers and investors should weigh the relative advantages of back-leverage against these inherent risks to determine what makes for a prudent investment decision.
Understanding the mechanics and implications of back leverage is critical for investors contemplating exposure to private credit funds an increasingly important part of this expanding market.
Read more about crypto and other categories at stock updates.






















Post Comment